An in-depth guide
Call quality
Want to improve your call quality? Sign up for a free 14-day trial of Dialpad to get an AI-powered collaboration platform with a built-in business phone system or, take a self-guided interactive tour of the app!
You can be the best in the business at what you do, but if you do a lot of business on the phone and your call quality is low, that’s the experience that’ll stick in your customers' minds.
At best, low-quality phone service is annoying—at worst, it compromises critical communication, which makes for a not-great customer experience… And can ultimately drive your customers away.
HD calling, which you can get with VoIP (or Voice over Internet Protocol) telephony technology, gives you crystal clear communication. But, it requires a reliable network and Internet service provider to make sure your call quality remains pristine.
This guide on call quality will show you how to overcome common call issues, and even how to measure and improve call quality.
But first, a little about the concept of call quality when it comes to HD or VoIP calling.
Understanding call quality
VoIP or Voice over Internet Protocol works by essentially breaking up the sound of your voice into thousands of tiny digital packets. These packets move along the network, hopefully through the most efficient path, to reach their destination. Once there, the packets are reassembled, and your words are communicated to the people on the other end of your call.
Good call quality requires a robust network that can reliably convey all packets to their destination to be put back together into a coherent whole.
👉 Dialpad tip:
Not all networks provide the same level of service and your local Internet service can also affect call quality. For example, you may have excellent call quality from the office, but not-as-good call quality from other locations, such as your home office, because the network isn’t optimized for HD calling. (Your Internet and router settings can also affect call quality.)
How to identify common call quality issues
Three common issues can wreak havoc on clear communication using VoIP: packet loss, jitter, and latency:
Packet loss
VoIP breaks sound into tiny digital packets that move along the network. They don't all necessarily move in order or even along the same route. The goal is to get those packets to their endpoint as quickly as possible. Once there, they are reassembled in the correct order for natural sound to issue from the speaker.
But what if some of the packets are lost? If there are network issues, packets may be dropped inadvertently on their way to the endpoint. Missing packets result in sound loss experienced by callers as a drop in audio.
If the packet loss is severe enough, the call is partially or even entirely dropped.
Jitter
You may have heard jitter during a call. It occurs when there is a change in the amount of time it takes for the packets to travel across the network. They get stuck somewhere, often because the network is congested.
The result is sound that arrives at the caller at irregular intervals, which creates a choppy audio sound.
Latency
Latency is somewhat related to jitter. It has to do with the amount of time it takes a packet to travel across the network. Instead of irregular intervals, the entire message arrives later than intended. Callers experience "double talk," even if they stop speaking ahead of hearing audio from the other end.
The audio delays make conversation tricky, with people accidentally speaking over each other.
With these three common issues in mind, how can you measure VoIP (HD) call quality?
How to measure call quality for VoIP
As we mentioned before, the quality of VoIP calls is highly dependent on your network. If you and your partner both work from home and regularly have video meetings, for instance, then you’ll probably need high-speed Internet in order to have the required bandwidth to handle HD calling. A slow or bad connection jeopardizes your ability to place calls and communicate clearly. The same applies to cell service.
The industry standard for measuring call quality is the Mean Opinion Score or MOS. It takes several critical metrics, including latency, jitter, and packet loss, to measure overall listening quality. Essentially, MOS is a numerical measure that quantifies the subjective experience of sound registering on the human ear.
How is Mean Opinion Score measured?
MOS is measured on a scale from 1.0 to 5.0. A score of 3.5 means around half of the users will complain about low voice quality. A high MOS score indicates the network is handling the call correctly. The listener receives all required sounds for clear communication.
👉 Dialpad tip:
Secondary metrics you might look at include measurements of the R-factor, which measures live, real-time user experience with the calls. It includes delay, echo, and recency. Then there’s measuring gap and burst density, which helps troubleshoot packet loss issues, whereas measuring the quality of service (QoS) monitors transmission quality.
Your VoIP service provider should measure these and other metrics for you to ensure that you experience high-quality communications. It should be a basic part of the customer experience. (For example, Dialpad's collaboration platform has a systems test that customers can use to check call quality.)
Want better call quality from your phone system?
Book a demo to see how Dialpad provides excellent call quality all over the world. Or, take a self-guided interactive tour of the app!
Troubleshooting: How to improve call quality
While your VoIP provider is responsible for many things that affect call quality, there are several ways you can do a little troubleshooting and try to fix poor call quality from your end.
Hang up the speakerphone
If you aren't having a group meeting, don't use the speakerphone for one-on-one calls. That’s because often, a laptop microphone is of pretty low quality and picks up background noise too. Occasionally, you or your listener will experience an echo effect, especially if you have your phone and computer microphone running simultaneously.
Take calls on a good pair of headphones or take the call on your mobile or desk phone.
Choose a good headset
If you’ve ever been in an open office setting, you know how distracting noise can be. The right headset can mitigate or eliminate much of the noise, and they often come with excellent microphones. Some headsets have noise-canceling features built in that include dual-mode active noise cancellation (ANC) that adjusts to your environment.
Wired headsets, either corded or USB, often deliver a clearer conversation than Bluetooth or other wireless models.
Reduce bandwidth across the network
Network congestion is a primary cause of jitter. When there's too much traffic across the network, collisions become inevitable, rather like a highway at rush hour.
Your IT department can use most network monitoring tools to identify the packet streams carrying VoIP data on the network. Once identified, this data can be tagged for protection using Quality of Service (QoS) features in the VoIP router.
They can manage bandwidth by measuring network activity and adding hardware and software to take some of the load. You can also adjust your router settings to, say, prioritize your VoIP calls instead of your kids video game streaming. (If you need a single, particularly robust line for video conferencing, you may be able to set up a dedicated virtual network just for VoIP traffic.)
Make sure the mobile experience is up to snuff
More and more employees are working on the go, and your employees have to be able to trust the quality of the mobile apps they use when they don't have access to office WiFi.
Dialpad offers both VoIP and carrier calling through its iOS and Android apps. When your employees leave the office, they can switch from WiFi to carrier seamlessly—and call quality remains intact.
A few other benefits of using mobile apps:
Seamless
—Dialpad lets you flip a call from your computer to your phone (and vice versa) seamlessly without interrupting or dropping the call:
with
, Google Workspace,
,
, and more:
Local presence and custom status support
Caller ID settings to differentiate between personal and business calls
👉 Fun fact:
Even Dialpad’s most basic plan comes with unlimited inbound and outbound calling within the US and Canada.
Test call quality before calling
VoIP services will require Internet access, and the network and devices that you’ve connected need to be adjusted to handle the calls. Otherwise, call quality may suffer.
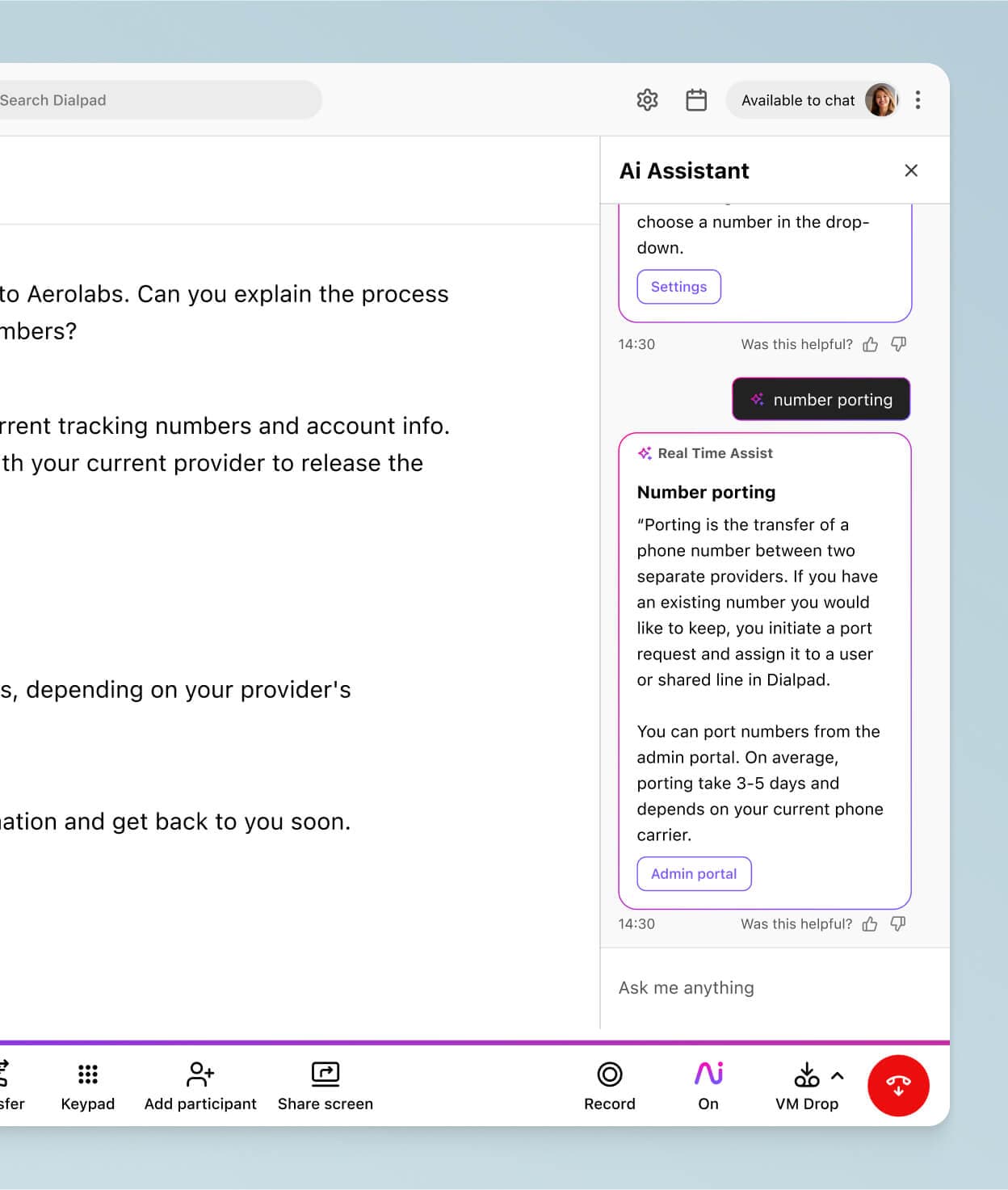
With Dialpad, as we mentioned earlier, you can run an individual test first without needing to contact your IT department, making it easy to test your network connection's health. To do so, follow these steps:
Open your desktop app or log into Dialpad on a web browser.
Select App Settings from the profile drop-down menu to display the option to test the network and audio connection.
A configuration wizard takes you through a step-by-step assessment of your microphone connection, audio playback, network connectivity, data transfer, VoIP, and audio input.
Submit and monitor call quality ratings
If you don't mention issues, they can't be fixed! Remember to rate call quality as soon as the call ends. On Dialpad, you can do this automatically, whether you’re on desktop or mobile.
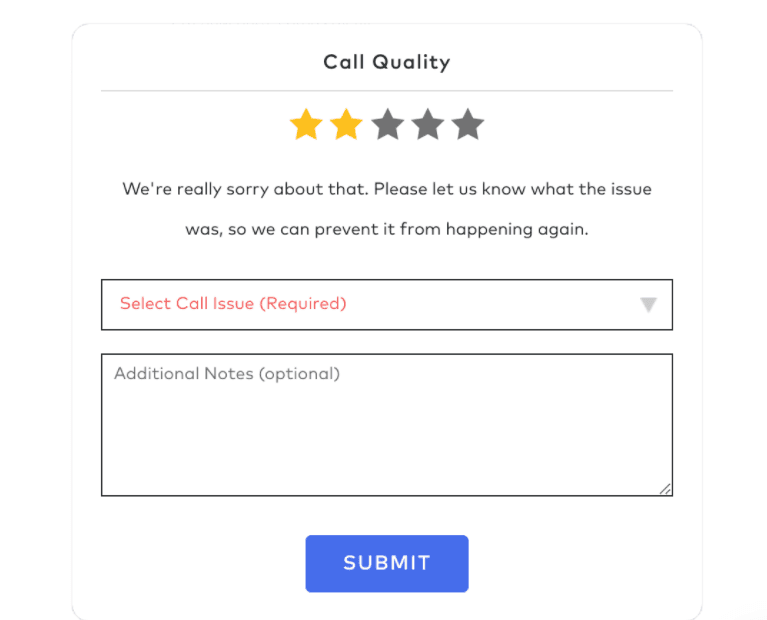
Calls with one or two-star ratings automatically include a drop-down menu with common issues that you can attach to the call record. Also, you can add details for our team in the Notes field.
Better call quality with Dialpad
Call quality is one of the most critical parts of the customer experience. It reflects directly on your business—even if any issues there aren’t your fault.
That’s why it’s important to choose a VoIP service provider that understands business communication means you have one less thing to worry about.
Dialpad is an AI-powered collaboration platform with a built-in VoIP phone system, a robust global voice network, and world-class customer service. Try it out and improve call quality for your business—no matter where in the world you are!
Ready to improve call quality?
Sign up for a free 14-day trial to try Dialpad out yourself. It takes just a few minutes to get set up with a virtual phone number and get started.
