2023 feels like the year that generative AI has broken through into the public consciousness. Tools like ChatGPT and Google Bard have taken the world by storm, becoming household names in just a few short months.
And, let's be clear, these recent developments are groundbreaking. They represent a massive advance in the possibilities—and our awareness—of generative AI. Anyone can use this technology to create new content. The potential impact of AI on our lives is clear for all to see.
We’re going to provide you with a primer on these recent developments in generative AI. First, what is it, and how does it work? Second, how could your business start using it, and what generative AI applications could there be in your day-to-day operations.
What is generative AI?
Artificial intelligence refers to computer systems or algorithms that can perform tasks which previously required human intelligence. It has been around for decades and is wide-ranging. Let's start by considering the bigger picture of AI and then situate “generative AI” within it.
The term “Artificial Intelligence” was coined as far back as 1956 and was already then the subject of much academic discussion. It progressed from there, in parallel with other developments in computer science.
In 1969, “Shakey”, the world's first general-purpose robot, was built, capable of problem-solving simple tasks. In 1997, the supercomputer “Deep Blue” was engineered, defeating Gary Kasparov (then world chess champion).
Such early work was impressive but of limited impact on everyday life.
Then, in the past few decades, progress accelerated. Artificial Intelligence has seeped into more and more areas of business and everyday life. Ever more powerful (and widely available) computers and devices facilitated this. And the increasingly online nature of our culture and economy fuelled it.
Let’s take one business example of AI’s reach. The chart below shows how AI was already embedded in many contact centres by 2022, often being used for routing, real-time agent assistance, AI transcription of calls, and more:
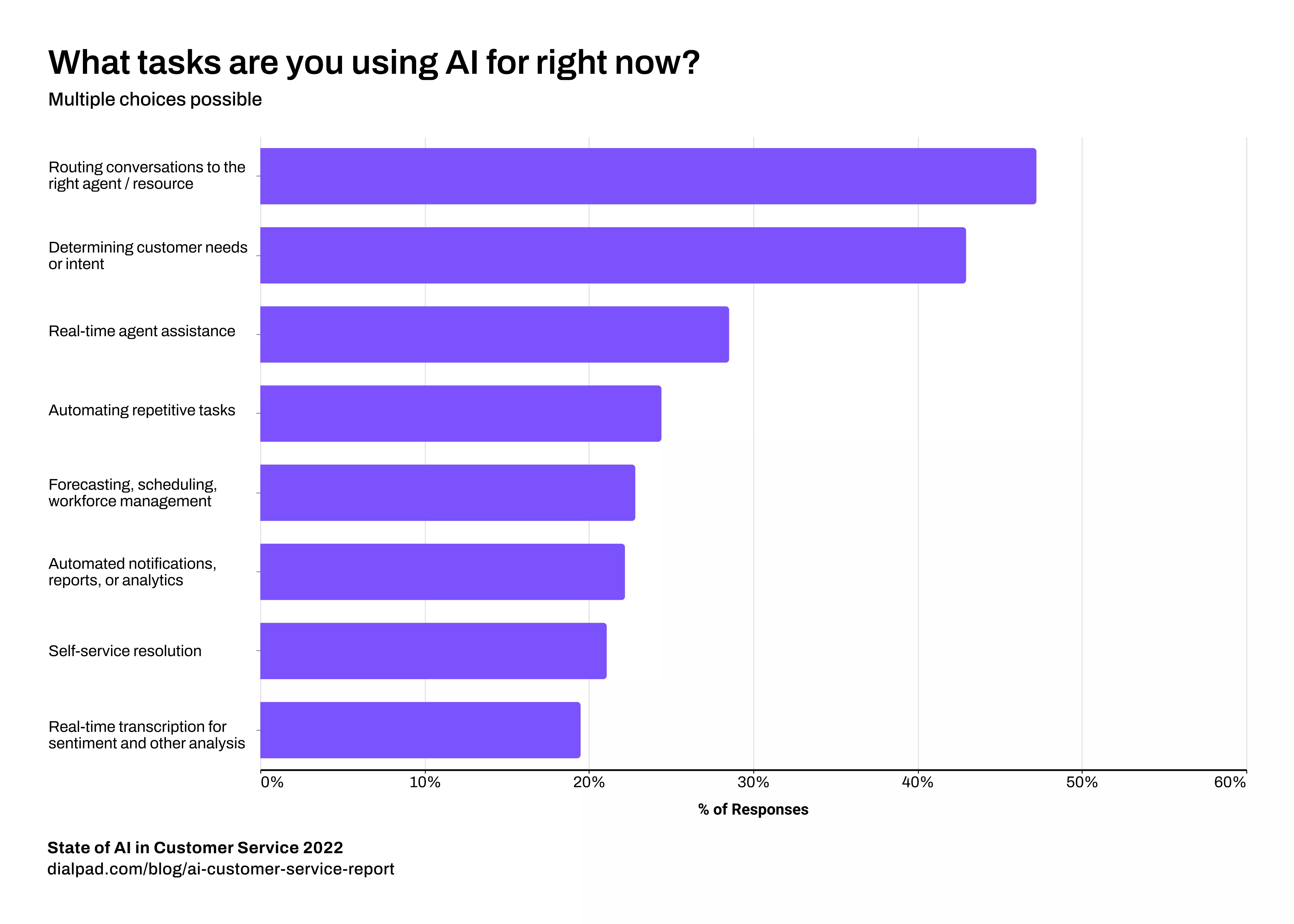
And, in fact, algorithm-powered AI plays a wide role in much of today's world:
AI-powered product suggestions while shopping online.
Organisations with large networks and infrastructures (such as oil refineries) use algorithms to monitor and predict potential problems.
Photo apps on your smartphones can use AI-powered facial recognition.
Algorithmic auto-predict and auto-correct functionality predicts the most likely words and phrases when typing messages.
We increasingly rely on such tools to monitor our surroundings and behaviour, and to make predictions based on that.
This AI technology has slotted into our lives and businesses. It has made a real impact, streamlining and supporting many tasks. See how Dialpad Ai has boosted contact centre efficiency in recent years:
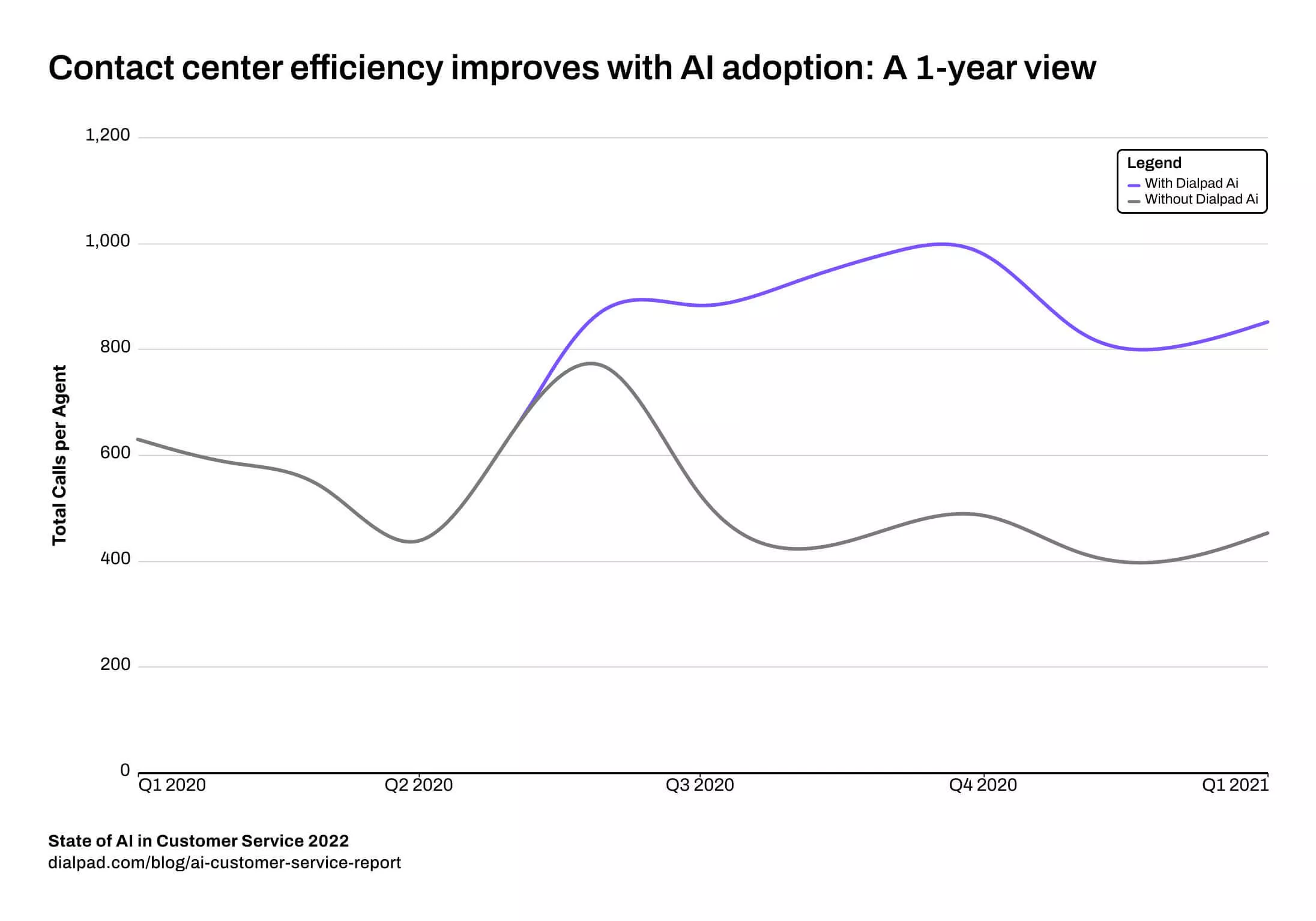
The recent developments in generative AI push things further. So far, we have been used to AI running in the background—monitoring, collating, analysing, and predicting. However, with tools such as ChatGPT, we can interact with AI in a way that goes beyond that.
These new AI tools step out from the shadows and seem to be creating. That is the essence of generative AI. It doesn't just monitor, analyse, and predict, it makes things with the appearance of human creativity.
What does it create? For your business, it might be advertising copy, summaries of research papers, real-time web chat support for customers, a product profile, and then perhaps re-versioning all those things in a different tone, style, or language.
Nor is this content generation technology limited to textual outputs. Generative AI, or gen AI, is also making strides in other areas including software coding, logos, pictures, artwork, music, videos, and even chemical formulations.
It looks set to expand into every area of human creativity: It writes, composes, designs, engineers, and codes. We've probably only scratched the surface of its potential.
How does generative AI work?
This more creative, generative aspect of AI is not wholly new. As long ago as the 1960s, attempts were made to pioneer it, such as in the case of ELIZA, the first therapist computer programme. But such early efforts were primitive. Generated responses felt limited, scripted, and shallow.
Improvements were made in subsequent decades. However, it was only in the 2010s that real strides towards the sort of generative AI we see today gained traction.
So why has generative AI become such a huge topic right now? A range of factors have facilitated its recent rise:
The computational power available has expanded massively. Modern computers can process mind-boggling quantities of data, which is key to training the massive models underpinning generative AI.
The continued accumulation of vast quantities of data. In our age of Big Data, nearly every transaction and interaction creates more. This data is the fuel (or training material) pushing AI models onward.
Better understanding of Deep Learning and neural networks, and in particular, the use of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to learn from existing content (I.e., the data already available) and generate new content.
Generative AI uses algorithms and models to produce new and original content based on patterns and examples from existing data. It leverages deep learning techniques to build immense foundational models, ultimately generating output that mimics human creativity.
GANs have played a key role. The GAN framework was first proposed in 2014 and pits two neural networks against each other in a game-like scenario (hence “adversarial”). That enables a competitive process whereby ever more credible content is generated.
The two competing networks involved in a GAN approach are described below:
The generator: This is trained to use existing “real” content (data) as a model for producing new content (text, images, or music outputs). The aim is to create fake (because it is wholly computer-generated) but realistic content, representative of the training data.
The discriminator: This is trained (using authentic, real-life data) to distinguish real-life data from the fake, computer-generated data.
After the discriminator has been trained, the adversarial stage can start. The discriminator is fed a mixture of authentic (real-life) and fake (from the generator) examples. It attempts to distinguish between the two: Which examples are genuine and which were faked by the generator?
This enables a refinement loop. At first, the discriminator will typically find it easy to identify the generator's fake data. When this happens, the generator is penalised and given feedback. The generator will then fine-tune its approach for producing its next batch of data, making it a little more authentic.
Thus, with each round, the generator becomes more successful at fooling the discriminator: The generator's outputs are ever-harder for the discriminator to classify as fake. Through this iterative process, the generator produces ever-more convincing output.
This is why tools like ChatGPT can appear so clever, authentic, and human-like in their responses. They were not built that way. Instead, they were trained, using vast amounts of data to iteratively learn how to mimic human creativity.
Generative AI examples: Tools already in use
Those, then, are the basics of generative AI. But how is it being used in the real world—particularly in business?
Let's look at just a handful of tools currently available:
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is the most famous example, currently, of generative AI.
It’s a language model trained on a massive dataset of text from the internet, enabling it to answer a wide range of queries in a conversational style. Type in a prompt, and it will respond. You can then ask it to refine its response by including a particular point or achieving a desired tone.
It’s widely used. ChatGPT has found applications in customer support, marketing content generation, education and training, and generating ideas. Need a product description, for example? Just type in some product details and parameters and it will generate some suggested copy for you.
Most users are impressed. And note that many other of the best generative AI tools are actually powered by ChatGPT behind the scenes. Nevertheless, it does have limitations. For example, it has a knowledge cut-off because it was trained using a dataset that only extended until September 2021. It has no knowledge of anything after that date.
Google Bard
Bard is Google's response to ChatGPT.
It offers another impressive conversational AI chat service. While it responds in a similar manner to ChatGPT, there are a few notable differences between the two tools:
Bard is generally seen as offering a more human-like chat experience.
Bard has online access (so there's no knowledge cut-off date).
ChatGPT is probably a more powerful text-processing tool for summarising and refining text.
Dialpad Ai
Businesses are increasingly exploring how generative AI can help with customer conversations. As long-time leaders in the AI arena, Dialpad is no exception. In fact, we’re partnering with Google Cloud to leverage generative AI.
New generative AI features will soon be rolling out to join our already extensive range of AI-powered functions. We already, for instance, offer a conversational AI-powered self-service tool that uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand customer queries and to generate appropriate responses.
Our Ai CSAT feature, meanwhile, helps deliver broader customer insights without the limitation imposed by customers’ reluctance to complete surveys. Not only that, Dialpad Ai can also generate post-meeting call summaries that provide a concise overview of what the meeting was about and any action items for attendees:
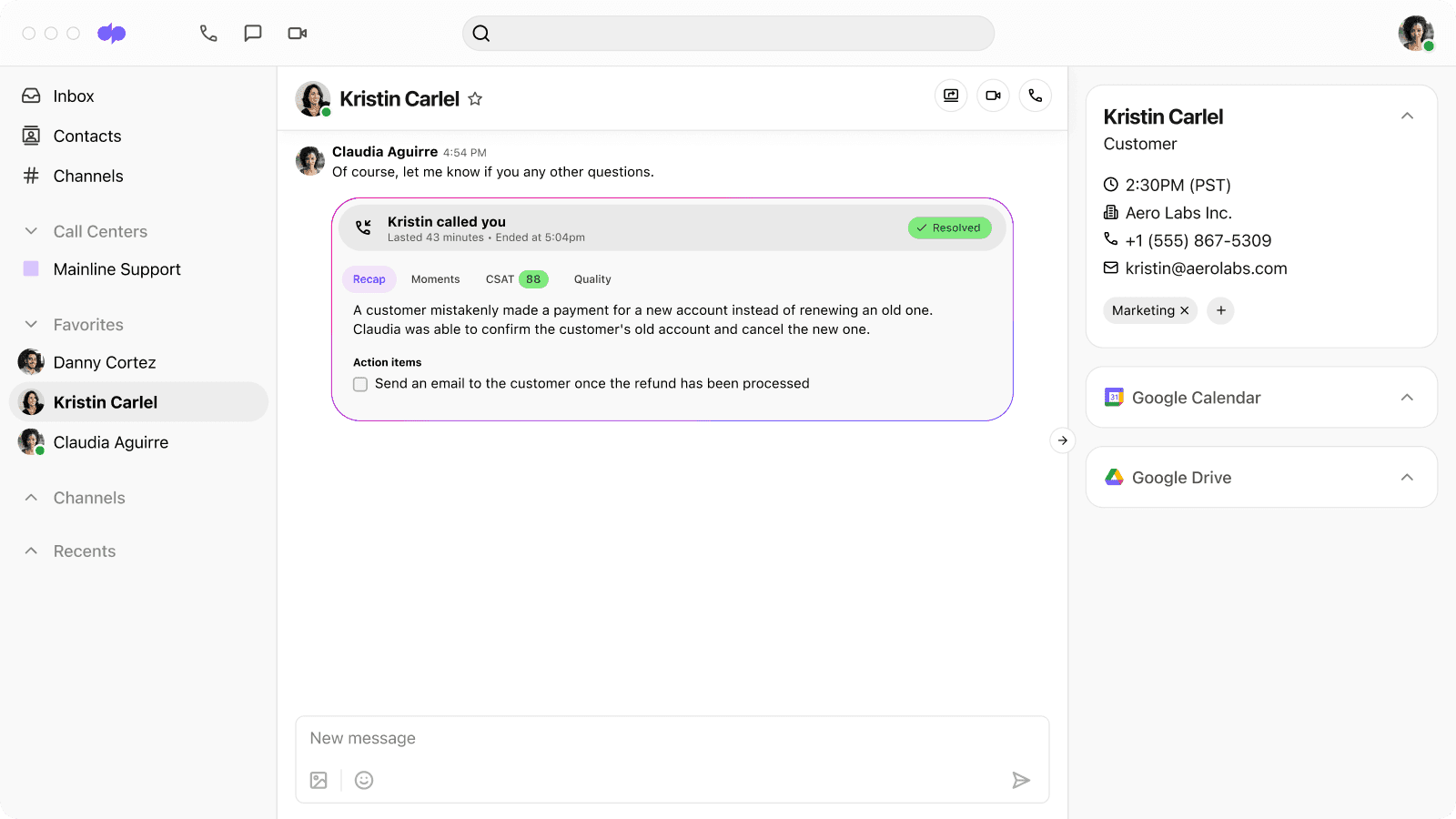
Soundraw
Need a soundtrack for a marketing campaign or event? Generative AI can help. Tools like Soundraw allow you to create royalty-free, AI-generated music to support your marketing.
You can specify a mood, genre, topic, length, tempo, and the instruments used to craft a piece that meets your needs. Then, you can choose from a wide range of given options.
Synthesia
Want to create a training or marketing video? Tools like Synthesia make that possible without turning a single camera on!
First, upload your script. The application creates a video featuring a life-like avatar presenter. And it's fully customisable so you can tweak your avatar's appearance, voice, and language.
Video creation has never been so easy and instant. A one-size-fits-all mentality is no longer necessary. Videos can easily be created and adapted to address the needs and circumstances of different segments or even individuals.
Potential generative AI applications for businesses
Let's run through just a couple of possible use cases of generative AI:
Content generation
Generative AI can automate content creation, including drafting blog posts, emails, social media content, product descriptions, and more. That can save you time and resources while maintaining consistency and quality, assuming you use generative AI tools well.
And all that generated content can be tailored to reflect the bespoke needs of each individual customer or recipient. In this way, generative AI looks set to turbo-charge personalised marketing.
Design and creativity
Generative AI can also be a valuable tool for designers, architects, artists, and scientists.
Once fed with requirements, parameters, and constraints, an AI system can produce multiple variations and options, helping designers explore possibilities and innovations.
Some see generative AI as a threat to human creativity. But this is not an inevitable consequence. It is most effective when supporting us and its output does not need to be the final product. Many businesses and entrepreneurs use generative AI to produce ideas and starting points—as an ever-available assistant.
Translation
Generative AI also has great potential in translation, enabling faster and more accurate translations. It can integrate seamlessly with Computer-Assisted Translation (CAT) Tools, allowing the AI to analyze and adapt to linguistic nuances and context.
This not only speeds up the translation process but also enhances quality, making it more natural and adapted to cultural specificities. This synergy between generative AI and CAT Tools is a significant advancement, promoting efficiency and accuracy in multilingual and globalized environments.
AI-powered virtual assistants
Generative AI can boost the capabilities of virtual assistants - compared to traditional chatbots. For example, Dialpad's AI technology can generate more useful, nuanced, and contextually appropriate support. These AI-powered conversational agents can provide more satisfactory, complete, and human-like interactions.
Support and training
Generative AI platforms can also support education and training; In schools, colleges, homes, businesses, hospitals, and more.
For example, your business could coach customer-facing agents using generative AI. By continually monitoring customer interactions (in real-time), for example, AI can guide the agent’s response:

Generative AI: A game-changer?
Generative AI is likely to be a game-changer for businesses when it comes to innovation, efficiency, and customer experience.
By leveraging vast amounts of existing data and learning from patterns, generative AI can inspire ideas and explore possibilities surpassing what humans could achieve alone. It can expedite the experimentation, prototyping, and iteration processand, indeed, has already accelerated the development and trialling of new medicines.
Automation via AI has already streamlined many business workflows, such as data entry, and generative AI will take that further. Now tasks requiring creativity can be (partially at least) automated. In particular, sales and marketing content can be automatically generated. This will undoubtedly boost efficiency.
Personalisation has become a central tenet of customer engagement in recent years. Using AI for customer experience enables your business to drive that agenda forward. Data will be at the heart of this, facilitating the generation of tailored content at an individual level.
Use generative AI to provide a better customer experience
Dialpad Ai is designed to help businesses do exactly this. Book a demo, or take a self-guided interactive tour of the app first!

