Agentic AI vs. generative AI: The key differences

Sr. Product Marketing Manager

Tags
Share
Ai has evolved rapidly over the past few years—from tools that generate text and images to systems that can plan and act. As this landscape matures, two major branches of Ai are starting to emerge more distinctly: generative Ai and agentic Ai.
If you’re leading a contact center, sales team, or any high-velocity communication function, understanding the difference between these technologies is vital. Each serves a different purpose and opens up different kinds of automation and intelligence.
Let’s unpack what makes them different, where they intersect, and how each one is used across modern workflows.
What is the difference between generative Ai and agentic Ai?
Generative Ai is designed to create content. It uses machine learning models (often trained on massive datasets) to produce new outputs based on input prompts. This includes generating human-like text, realistic images, voice responses, or even code. Tools like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and Midjourney are well-known examples. In business, generative Ai often shows up in features like email drafting, meeting summaries, call transcripts, or chatbot scripting.
Agentic Ai, on the other hand, refers to Ai systems that can plan, initiate, and complete multi-step tasks autonomously. Instead of just generating an output when asked, agentic Ai acts more like a collaborator—analyzing goals, breaking them into steps, making decisions based on feedback loops, and adapting to changing conditions without constant human input.
In other words:
Generative Ai creates content (like text, images, or videos).
Agentic Ai decides what to do, and does it (sometimes by using generative Ai along the way).
Agentic Ai vs. generative Ai comparison
While both types of Ai rely on advanced machine learning, they differ in architecture, functionality, and operational scope. Here's how they stack up:
Generative Ai
Primary function: Content generation based on prompts
User interaction: Requires human input or direction to generate output
Memory/context: Typically stateless or session-based
Use case examples: Writing sales emails, summarizing meetings, generating knowledge base articles
Tools: ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Claude, Jasper, Copy.ai
Agentic Ai
Primary function: Goal-driven task execution through autonomous planning
User interaction: Minimal input needed; system can self-direct and iterate
Memory/context: Requires persistent memory, task queues, and state tracking
Use case examples: Handling multi-threaded customer service tickets, reprioritizing tasks in real time, automating follow-up sequences
Tools: Dialpad Support, AutoGPT, LangChain agents, ReAct frameworks, Zapier
Where you’ll see them in action: Agentic Ai vs. generative Ai examples
Both types of Ai are powerful, but they shine in different areas. Let’s look at some examples of how they’re used in contact centers, sales outreach, internal communications, and industries adopting Ai at scale:
Contact centers
Generative Ai – Can automatically summarize support calls, suggest responses in real time, generate help center articles, and transcribe voice interactions
Example: Dialpad Support uses generative Ai to create real-time transcripts and call summaries to help agents stay focused.
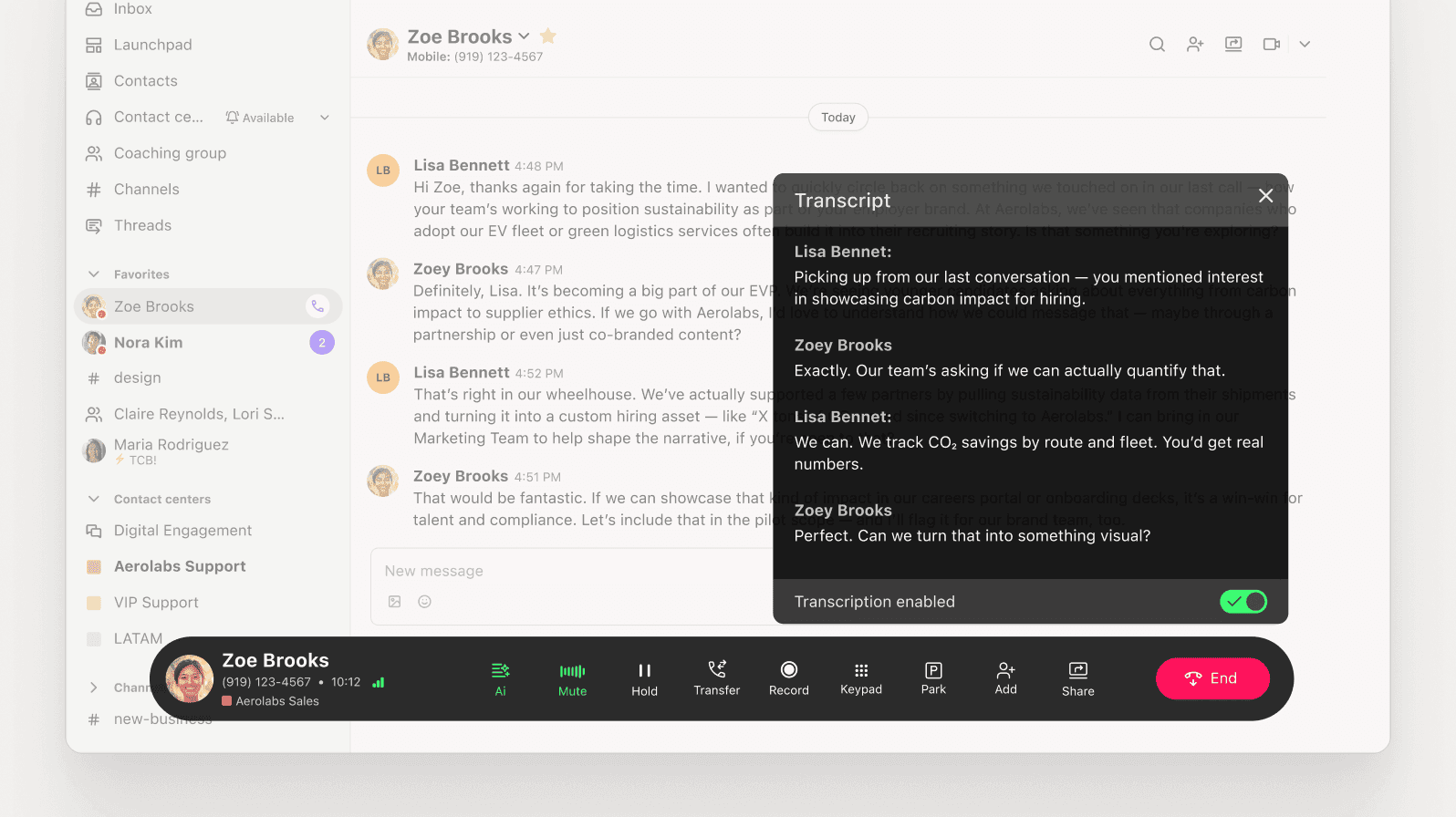
Agentic Ai – Can manage full ticket workflows, including monitoring support queues, logging details in the CRM, and closing the case without human intervention
Example: An agentic Ai could detect a pattern of negative sentiment across multiple customer chats, auto-prioritize those tickets, initiate a resolution process, and notify a supervisor before it becomes a broader churn issue.
Fun fact: Dialpad is currently developing an agentic Ai platform to allow customers to create practical, fully autonomous, applications such as:
Order tracking – Automatically authenticating customers, accessing order systems, and providing real-time shipping updates with delivery estimates and tracking options.
Appointment management – Rescheduling appointments, showing available time slots, and updating scheduling systems automatically.
Recruitment screening – Conducting initial candidate interviews, collecting qualifications, storing information in HR systems, and scheduling applicants for interviews with the recruitment team.
Sales outreach
Generative Ai – Can write cold email drafts, personalize outreach messages, and create pitch decks
Example: A sales outreach tool that uses generative Ai to help reps draft follow-up emails and generate call recaps post-demo.
Agentic Ai – Can automate and adjust outreach sequences based on lead behavior
Example: An agentic system could manage a rep’s follow-up strategy across an entire pipeline, initiating reminders, re-prioritizing hot leads, and scheduling demos based on Ai analysis of intent signals.
Internal communications
Generative Ai – Can summarize meetings, draft internal newsletters, and create knowledge articles from documentation
Example: Automatically creating an internal summary after a cross-functional team call.
Agentic Ai – Can coordinate follow-ups, schedule meetings based on availability and context, and nudge stakeholders to complete assigned tasks
Example: After a team meeting, an agentic Ai generates action items, assigns them to team members, and follows up on deadlines.
Healthcare operations
Generative Ai – Can write patient summaries, transcribe doctor-patient interactions, drafts clinical notes, and generate educational materials tailored to patient diagnoses
Example: A clinician uses generative Ai to create post-visit instructions for a patient based on the notes from a telehealth session.
Agentic Ai – Can manage patient intake, automate scheduling and reminders, and coordinate multi-step care plans across departments
Example: An agentic system could automatically follow up with patients for lab work, update the provider’s schedule, and notify staff when test results require urgent attention.
HR and Recruiting
Generative Ai – Can create job descriptions, draft offer letters, write candidate communications, and generate interview questions based on role requirements
Example: A recruiter uses generative Ai to instantly draft a personalized follow-up email to a candidate after their first-round interview, pulling in role details and notes from the hiring manager.
Agentic Ai – Can manage end-to-end recruiting workflows including screening resumes, scheduling interviews, tracking progress in the ATS, and following up with hiring teams and candidates
Example: An agentic Ai reviews inbound applications, shortlists qualified candidates based on job fit, schedules them for initial interviews, and nudges hiring managers to complete feedback forms — all without manual coordination.
Financial services
Generative Ai – Can create personalized investment summaries, customer reports, and educational content for clients
Example: A financial advisor uses generative Ai to generate a tailored retirement outlook summary based on portfolio data.
Agentic Ai – Can handle fraud detection workflows, automate compliance reporting, and onboard a new client (e.g., collecting documents and verification).
Example: An agentic Ai monitors transactions for suspicious activity, triggers verification requests, and escalates issues to the fraud team only when human review is needed.
E-Commerce and retail
Generative Ai – Can write product descriptions, auto-generate customer responses for product questions, and personalize abandoned cart emails
Example: A marketing team uses generative Ai to create unique product copy at scale for a catalog of thousands of SKUs.
Agentic Ai – Can track customer behavior, manage automated return/refund flows, and optimize fulfillment logistics based on order patterns and inventory
Example: After identifying repeated return requests for a product, an agentic Ai initiates a product flag for review and begins proactive outreach to impacted customers.
Logistics and supply chain
Generative Ai – Can draft shipment updates, generates route documentation, or creates reports for internal logistics planning
Example: A warehouse uses generative Ai to produce shift briefings and incident logs based on system data.
Agentic Ai – Can orchestrate end-to-end delivery planning including inventory balancing, re-routing based on traffic/weather, and supplier coordination
Example: An agentic Ai reassigns shipments in real time due to supply chain delays and automatically notifies vendors and customers of new ETAs.
Risks and limitations: Where each can fall short
No Ai system is perfect. Understanding where each approach has blind spots is essential for making smart implementation decisions.
Generative Ai risks
Generative Ai can produce high-quality outputs, but it’s not always reliable. Without context or oversight into training datasets, it may “hallucinate” facts, offer outdated information, or generate content that sounds confident but is incorrect. It also lacks memory by default, which means it can’t learn from previous interactions unless it’s paired with external systems. For customer-facing teams, this means that any output from a generative Ai model (whether it’s a support summary or a sales email) should still be double-checked.
Agentic Ai risks
Agentic Ai adds autonomy and decision-making, but that also introduces more complexity. These systems are designed to act on their own, monitoring workflows, triggering follow-ups, reprioritizing tasks, and orchestrating outcomes. Without proper constraints, poorly designed agentic systems could misinterpret data or take actions that are out of sync with business policies.
It’s important to note that these risks are not inherent to agentic Ai—they often stem from poor implementation or tools. Look for secure, enterprise-grade Ai platforms that support clear task boundaries, audit trails, and integration governance to mitigate and minimize risk.
At Dialpad, for example, agentic Ai features are being developed with robust data privacy, role-based access controls, and transparent decision logic. That means organizations can deploy Ai agents confidently—knowing they’ll operate within approved workflows, respect security policies, and escalate when human judgment is needed.
The bottom line: Both types of Ai tools require governance, testing, and (especially early on) human supervision.
Why this matters for the future of work
Generative Ai made the first big wave, giving teams a massive productivity boost by automating content creation. But as workflows become more complex, businesses are looking for systems that go beyond answering prompts. That’s where agentic Ai comes in.
Beyond taking on basic tasks, agentic Ai is a systems-level thinker that can orchestrate multiple tools, manage workflows, and learn from results. It’s especially powerful in high-stakes, high-volume environments like contact centers and outbound sales teams, where timing, prioritization, and follow-through are critical. In fact, Gartner predicts that by 2029, agentic AI will autonomously resolve 80% of common customer service issues without human intervention, leading to a 30% reduction in operational costs.
That doesn’t mean generative Ai is going away. In fact, many agentic Ai systems rely on generative models to carry out parts of their work. But the shift from reactive content generation to autonomous action marks a significant step forward in how Ai will support business operations moving forward.
Agentic Ai: Dialpad’s autonomous agent assistance system
Agentic Ai is Dialpad’s next-generation innovation. It is an in-house-built, autonomous agent assistance system that transforms how organizations work. It’s designed for real-time engagement and works seamlessly across all customer channels.
✅ Key Features of Agentic Ai:
Wherever customers need:
Deliver a unified experience across voice, video, and digital messaging channels, ensuring customers get consistent, intelligent responses—no matter how they reach out.Natural conversation:
Provide a natural, low-latency voice experience that feels truly human. It's purpose-built for high-quality real-time interactions, not retrofitted from chat.Autonomous assistance:
Agentic Ai supports customers and agents in real time with intelligent actions like handling routine queries, scheduling appointments, and checking order status—without needing human intervention.Seamless escalation to human agents:
When escalation is required, Dialpad’s Ai Agent instantly hands off to human agents with full conversational history and context—eliminating redundancy and improving resolution times.
Scalability with insight:
Easily deploy multiple bots for multiple channels, without sacrificing on insights. Drive better business outcomes from analytics across any interaction: voice, chat, and more.
Agentic Ai vs. generative Ai: Are you using both?
The most forward-thinking organizations aren’t choosing between the two — they’re designing workflows that combine them. Imagine an Ai that writes your sales emails and knows when and how to send them based on lead behavior. Or one that transcribes your support calls and kicks off follow-up workflows automatically.
That’s not a distant future. With tools like Dialpad Ai, it’s already starting to happen.
Try the industry-leading contact center platform powered by agentic Ai
From intelligent agentic Ai to real-time transcription and proactive follow-ups, Dialpad Support empowers your team to resolve issues faster and deliver exceptional customer experiences—all in one seamless workspace.
